모델 구조
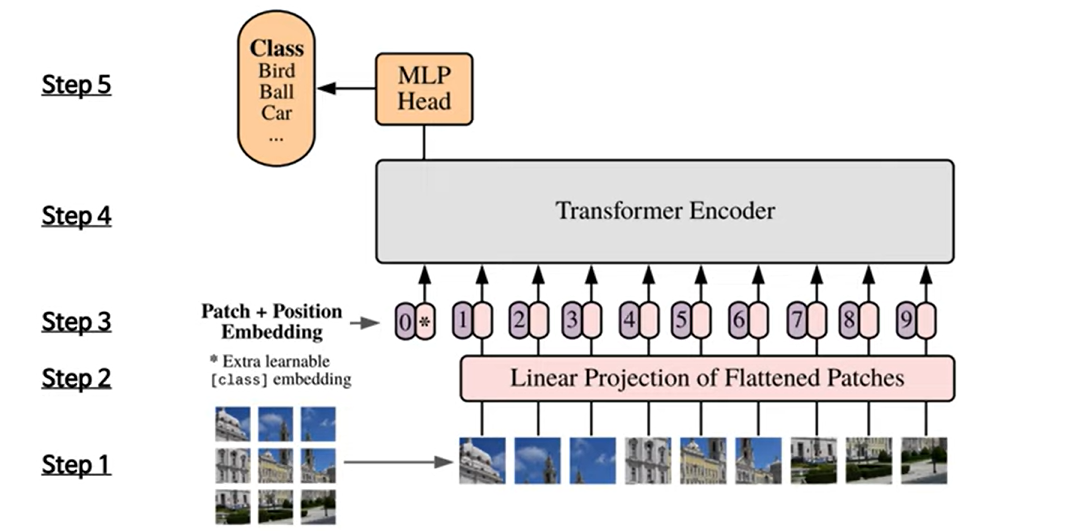
Step1
- 특정 크기의 이미지를 N(=HXW/P^2)개로 분할해 패치 sequence xp∈RN×(P2⋅C)
Step2
- Trainable linear projection을 통해 xp의 각 패치를 flatten한 벡터를 D차원으로 변환한 후 이를 패치 임베딩으로 사용한다.
Step3
- Learnable class 임베딩과 패치 임베딩에 learnable position 임베딩을 더한다.
Step4
- 임베딩을 vanila Transformer encoder에 input으로 넣어 마지막 layer에서 class embedding에 대한 output인 image representation을 도출한다.
Step5
- MLP에 image representaion을 input으로 넣어 이미지의 class를 분류한다.
4가지 Embedding
No positional information
- position embeding 사용하지 않고 input된 position그대로 사용함
1-dimensional positional embedidngs
- 순서대로 patch(input된 것)을 순서대로 본다.
2-dimensional positional embedidngs
- patch의 x축과 y축을 고려해 embeding을 하는 것이다.
Relative positional embedidngs
- patch사이에 상대적 거리를 사용한 positional embedding
최종적 사용
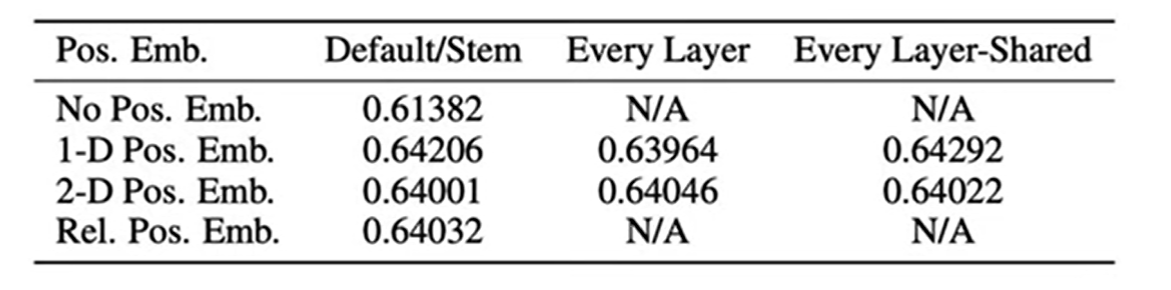
- learnable positional embedding에 1-dimensional positional embedidngs의 결과를 사용한다.
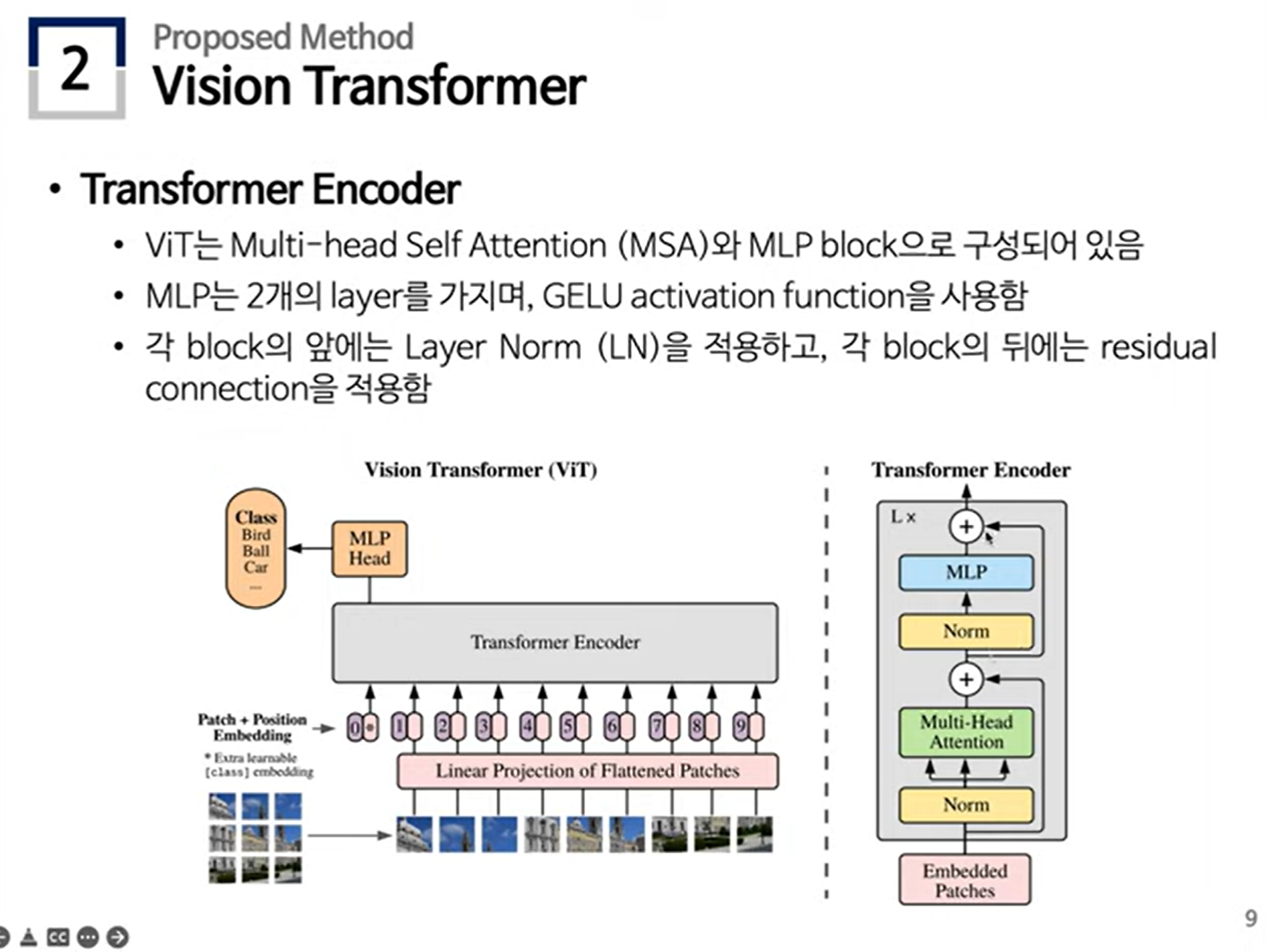
사용된 Transformer Encoder 구조
Hybrid Architecture
- CNN으로 추출한 raw이미지의 feature map을 활용해 사용할 수있다.
- raw image는 공간적 정보를 포함해 hybrid architecture는 패치크기를 1X1로 설정해도 된다. 이 경우 feature map의 공간 차원을 flatten해 각 벡터에 linear projection을 적용하면 된다.
Fine-tuning and Higher Resolution
- Large scale로 ViT를 pre-training한 후, 해당 모델을 downstream task에 fine-tuning하여 사용할 수 있다.
- ViT를 fine-tuning 할 때, ViT의 pre-trained prediction head를 zero-initialized feedforward layer로 대체하고 pre-training과 동일한 패치의 크기를 사용하기 때문에 고해상도의 이미지로 fine-tuning을 하면 sequence 길이가 더 길어진다.
- ViT는 가변적 길이의 패치들을 처리할 수 있지만, pre-trained position embedding은 의미가 사라지므로 pre-trained position embedding을 원본 이미지의 위치에 따라 2D interpolation하여 사용한다.
실험결과
- 데이터가 클 수록 정확도가 좋아졌다.
- 데이터로 부터 학습하는 것만으로도 충분히 패턴 학습이 가능하다.
출처
Paper Review] ViT: An Image is Worth 16x16 Words:Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale
소감
- 논문 리뷰보단 영상 요약이 되었다.
- 열심히 하자....;;;;ㅠㅠㅠㅠ